By Melissa Arnold
We’ve all experienced it at some point in our lives, even briefly: That nagging feeling of discontent about the way you look.
Maybe you’re a parent with stubborn post-baby weight, someone who’s had gastric bypass surgery with lots of extra skin or even someone recovering from a traumatic injury that’s affected your appearance. In all of these cases, lifestyle changes can only do so much.
For many years, plastic surgery has bridged that gap, giving patients from all walks of life the look they’ve longed for. And while it’s still going to cost you, going under the knife is simpler than ever.
An ancient practice
Believe it or not, plastic surgery has been around for thousands of years in two forms — reconstructive and cosmetic. According to the National Institutes of Health, some of the earliest body-altering procedures were performed in India around 800 B.C. At that time, people often had their noses cut off during conflict or as punishment, and simplistic rhinoplasties, “nose jobs,” were performed to reconstruct them.
Modern reconstructive surgery was born in wartime as soldiers dealt with facial trauma and other injuries. The American Board of Plastic Surgery was organized in 1937.
Cosmetic surgery took longer to become popular — the buzz surrounding it didn’t pick up until the 1970s and 80s, says Dr. Jim Romanelli of North Shore Plastic Surgery in Huntington.
“There was [originally] some resistance within medicine, saying it was unnecessary, dangerous and vain,” Romanelli said. “But today, we know a lot more about performing the surgery safely with good results.”
What began with involved, painful procedures and long scars has grown into a streamlined, patient-directed field of surgery with more natural-looking results and less hassle.
And these days, plastic surgery and cosmetic procedures are more accessible than ever. While no cosmetic surgeries are covered by insurance, there are now plenty of options to finance them, from saving up cash to working with a lender or financing company.
“Most people having cosmetic surgery just want to look in the mirror and feel happy and healthy,” Romanelli said. “These are everyday people — schoolteachers, musicians, bus drivers — not exclusively wealthy people or celebrities.”
While many patients opting for surgery are women, the number of male patients is growing too.
Modern trends
In the past, a patient’s wishes weren’t always a huge priority. Years ago, a surgeon may have only performed a procedure in a certain way. If the patient hoped for something different, they’d have to look elsewhere.
But today, it’s not uncommon for patients to bring in photos of the kind of look they’re hoping for, much like choosing a hairstyle or wedding dress, Romanelli explained.
Finding out what the patient really wants is the foundation of modern cosmetic surgery, says Dr. Hilton Adler of Suffolk Plastic Surgeons in Setauket.
“I always start by asking a patient what they’re looking for — what concerns them and what they want to see changed,” he said. “Then, following an exam, I’ll offer them choices based on what [technology is] available.”
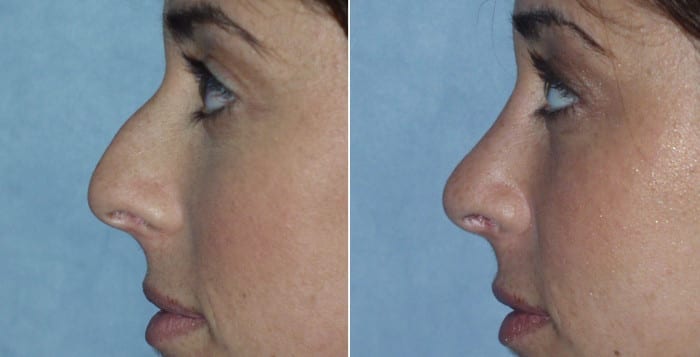
Today’s most sought after surgeries aren’t that different from the past. Nose jobs, breast reductions or augmentations, tummy tucks and face-lifts all top the list.
“I wouldn’t say that any particular cosmetic procedure has been abandoned, just significantly modified. It’s almost like a brand-new procedure in some cases,” Adler explained.
For example, Romanelli says that the incisions used for breast-related surgeries have changed, allowing for a smaller scar. In some cases, the incision is made under the arm, where it’s less obvious.
There’s also the “mommy makeover,” which combines a tummy tuck and a face lift or breast work into one surgery.
Men usually come in for facial work, but many are also seeking help for gynecomastia, a condition that causes breast development.
“It’s tough on guys who are in high school or college whose breasts develop,” said Dr. Gregory Diehl of Diehl Plastic Surgery in Port Jefferson Station. “The hormones are fine, but the glands are bigger. Its become more common today to look for a fix.”
In reconstructive surgery, one of the most common procedures today helps to eliminate excess skin that often occurs in people who have experienced rapid or significant weight loss, Adler says. In many cases, the weight loss is aided by gastric bypass procedures.
Noninvasive procedures and more
Of course, not every cosmetic procedure requires surgery. In fact, minimally invasive and noninvasive procedures are extremely popular today, as new technology continues to develop.
“People are trying to get away from surgery, while things like Botox and other (injectable) fillers are becoming more popular,” Diehl said.
Injectables are a group of materials that can smooth wrinkles, plump other areas, and create a more youthful look overall.
Procedures such as CoolSculpting, which freezes and shrinks fat cells, and ultherapy, which uses ultrasound technology for tightening the face, are also on the rise, Adler said.
Put simply, if you can dream it, there’s likely a procedure to help you achieve it.
Planning your makeover
If you’re looking to have cosmetic surgery or another procedure, the first step is choosing the right surgeon.
“We urge patients to seek out board-certified plastic surgeons. Make sure your doctor has proper credentials,” Adler said.
Diehl also noted that they should offer to show you their previous work. “Ask for pictures of their surgeries. You should like what you see. Pictures tell the story,” he said. “Also, is the doctor really listening to you and what you want? You have to communicate. You have to make sure all the details are ironed out.”
Once you find the right person, a consultation lasts anywhere from 30 minutes to an hour.
The surgeon will get an idea of what you’d like to do, and in some cases allow you to check it out using computer imaging.
If you’re satisfied, you’ll return for a second appointment to address any new questions or concerns before scheduling the procedure. The exact process and recovery time varies, depending on the procedure. Many surgeons have operating rooms in their own offices, and barring complications, a patient can go home the same day.
Making a difference
The surgeons are quick to note that there’s no longer any stigma surrounding plastic surgery. “People are proud of what they’ve done. They want to tell everyone about it,” Diehl said.
The surgeons are proud, too.
“People do say, ‘You’ve changed my life. I should have done this sooner.’ It’s wonderful to be able to help people with that,” Romanelli said.