Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine booster shot available to frontline health care workers
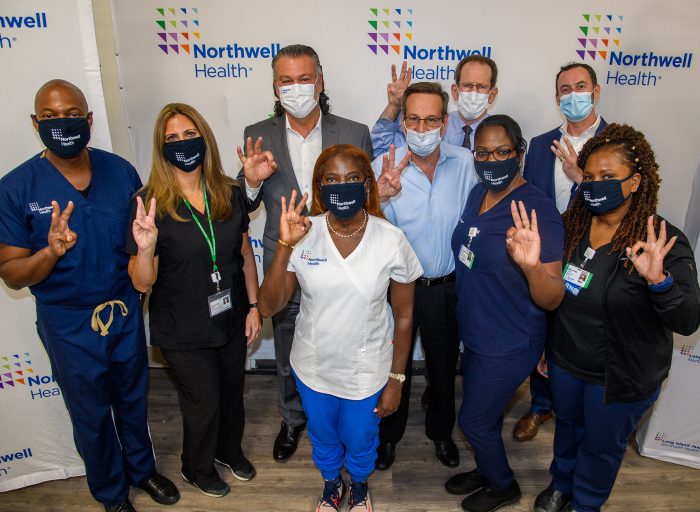
More than nine months after she became the first American to receive the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, Sandra Lindsay, RN, director of nursing critical care at Northwell Health’s Long Island Jewish Medical Center (LIJ), today received a booster shot to increase her immunity against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
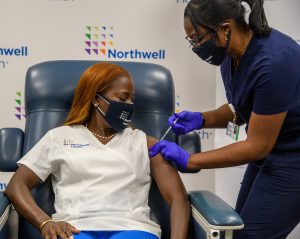
Ms. Lindsay enthusiastically held high three fingers moments after Michelle Chester, DNP, director of Northwell Health Employee Health Services, administered the booster shot in front of reporters. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved an additional shot of Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine on September 22 for those 65 and older, individuals at high risk of severe disease and those whose work may lead to frequent exposure to the virus.
“I am delighted to receive the booster today as yet another chapter in the fight against COVID-19,” said Ms. Lindsay, who was honored by President Joe Biden in a White House ceremony and served as grand marshal of NYC’s Hometown Heroes Parade, both in July. “For me, personally, it’s been an incredible journey and a privilege. It’s my belief that if I can change one person’s mind who is hesitating to become vaccinated and help encourage them to follow the science, it’s been a good day.”
Ms. Lindsay became a household name on December 14, 2020, when she was shown receiving the first Pfizer dose in the United States as part of a video conference call with then-New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo. Items used as part of her vaccination were donated to the Smithsonian’s National Museum of American History.
On Wednesday, Ms. Lindsay was back in front of cameras, one of five frontline health care workers who publicly received their booster shot. The others were: Yves Duroseau, MD, chief of emergency medicine at Lenox Hill Hospital in Manhattan and the second American vaccinated; Elyse Isopo, NP, North Shore University Hospital in Manhasset; Richard Schwarz, MD, medical director at LIJ; and Andrew Adesman, MD, chief of behavioral pediatrics at Cohen Children’s Medical Center in New Hyde Park.
“We are all so proud of each member of our Northwell family who agreed to participate in getting vaccinated to help us fight the battle of this pandemic,” said David Battinelli, MD, senior vice president and chief medical officer. “During this year, we saw the true heroism of each member of our staff – doctors, nurses, therapists, dietary, environmental services – all doing their best to fight this unknown disease, at their own risk. During this last year-and-a-half, we truly saw fear morph into courage. And now, after this most difficult year, we are delighted to be able to offer our team members a booster shot of the Pfizer vaccine. We urge everyone to follow the science and get their booster shot when they become eligible.”
Northwell Health, the largest health system and private employer in New York State, announced on Monday that its staff is now 100 percent vaccinated, in compliance with New York State Governor Kathy Hochul’s mandate that all health care workers be vaccinated.