Ask the Vet: Have ticks become a year-round problem?
By Matthew Kearns, DVM
 I commonly get the question, “What month can I stop using tick preventatives?” My answer is always, “That depends.” It used to be that somewhere around late October/November until late March/early April one could stop using flea and tick preventatives. However, with changing climate conditions and parasite adaptation this is no longer true.
I commonly get the question, “What month can I stop using tick preventatives?” My answer is always, “That depends.” It used to be that somewhere around late October/November until late March/early April one could stop using flea and tick preventatives. However, with changing climate conditions and parasite adaptation this is no longer true.
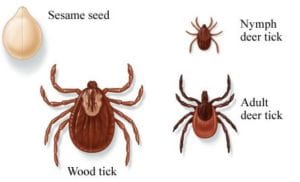
The tick life cycle contains four stages: egg, larval, nymph (young adult) and adult. After the larval stage hatches out from the egg, it must feed and go through a molt between each successive stage. Ticks are sensitive to environmental changes throughout their life cycle but, ironically, are most resistant to temperature changes. It has to be below 35°F for ticks to even “overwinter.”
Overwinter is a term that refers to a process many species use to pass through the period of the year when “winter” conditions (cold or sub-zero temperatures, ice, snow, limited food supplies) make normal activity or even survival difficult or near impossible. During the overwinter period all activity nearly completely ceases until conditions become more favorable. If conditions become more favorable (above 45°F) ticks will set out in search of a host.
 To kill a tick temperatures must be consistently below 10°F for many days in a row. If the tick is able to bury itself in the vegetation below a layer of snow, even below 10 degrees may not kill them. It is pretty routine even in January to have one or two days that are in the 20s during the day, dropping to the teens or single digits at night followed by a few days in the 50s.
To kill a tick temperatures must be consistently below 10°F for many days in a row. If the tick is able to bury itself in the vegetation below a layer of snow, even below 10 degrees may not kill them. It is pretty routine even in January to have one or two days that are in the 20s during the day, dropping to the teens or single digits at night followed by a few days in the 50s.
Ironically, as resistant as ticks are to colder temperatures, they are much more sensitive to higher temperatures and humidity (or lack thereof). Eggs will desiccate, or dry out, and die during hot dry periods. The other life stages are at risk for dehydration due to increased respiratory rate in an effort to thermoregulate (control body temperature) and questing (looking for hosts).
Hotter, drier temperatures mean less vegetation. Less vegetation causes multiple problems for ticks: less protection from the elements and less vegetation for hosts.
The white-footed mouse is the primary host for the larval stage of the deer tick. This mouse survives on vegetation, and less vegetation and less resources for the mouse means a subsequent decrease in the mouse population. A decrease in population means less hosts. Less hosts, less ticks survive from the larval stage to adulthood. Fortunately, and unfortunately for us, the northeast United States rarely sees prolonged droughts. Even if we have hot, dry periods during the summer, we usually make up for it in the fall. It is an ideal environment for many species of ticks, specifically the deer tick.
In summary, it is my feeling that the tick season is 9 to 10 months out of the year. You may be able to stop applying preventative during the months of January, February, and March (this depends on temperature), but the rest of the year ticks are active.
Dr. Kearns practices veterinary medicine from his Port Jefferson office and is pictured with his son Matthew and his dog Jasmine.







